Wordmeainginterpretation
Federalgovernmentreferstothecentralgovernmentofafederalcountry.Thefederalgovernmentusuallyappearsindemocraticcountriesundertheruleoflaw,orincountrieswithstronglocalawareness.Incontrasttocentralization,federalismisasystemofdecentralization.Itsconstitutiondividesmostgovernmentpowerstolocalgovernments.Thecentralgovernmentcanonlyberesponsibleforlimitedaffairs.Financialpower.Thefirstlevelofgovernmentiscalledthefederalgovernment,whichisthecentralgovernmentacrossthecountry.Thesecondlevelofgovernmentisthestategovernment,whichisanintegralpartofthefederalgovernment.
Formofcomposition
IntheUnitedStates,thefederationiscomposedofvariousstates.Asalocalcomponentofthecountry,the"state"canonlybeusedinthenameofacertainstateintheinternationalcommunity.Activity.IfacertainstateintheUnitedStateswantstosecedefromtheUnion,thefederalgovernmentwilldefinitelyintervene,andtheinternationalcommunitywillnotrecognizeitsnationalstatus.UnlesstheUSfederalgovernmentitselfrecognizesit,theinternationalcommunitywillbeabletorecognizeitsqualificationsasasubjectofinternationallawafteritsrecognition.IntheformerYugoslavia,thecountryconsistsofseveralcountriesformingafederation.Eachcountryhasitsownconstitutionanditsownnationalautonomy.Theyuniteonlytobetterfightforrightsintheinternationalcommunity.Recently,thetwofederalentitiesofSerbiaandMontenegro(SerbiaandMontenegroforshort)split,andeachbecameindependentastheRepublicofSerbiaandMontenegro,whichwasrecognizedbytheinternationalcommunity.
Systemform
Unitarysystem
Thenationalstructureformofthegeneraladministrativeregionorautonomousregiondividedbyregionastheconstituentunit.Contrastwithcompoundsystem.Inaunitarycountry,thecentralgovernmentenjoysthehighestauthority,andthelocalgovernmentexercisesitspowersundertheunifiedleadershipofthecentralgovernmentandwithinthescopeofauthorityprescribedbytheconstitutionandlaws.Legally,allpowerinaunitarycountrybelongstothecentralgovernment,andlocalpowerisauthorizedbythecentralgovernment.Theobviousexternalcharacteristicsofaunitarycountryare:thecountryhasonlyonecentralpower,oneconstitution,andonelegalsystem.Itisthesubjectofinternationalrelationsininternationalexchanges,anditscitizenshaveonlyonenationality.Thisformisadoptedbymostmoderncountries.Accordingtothesizeoflocalauthority,unitarycountriescanbedividedintocentralizedunitarycountriesanddecentralizedunitarycountries.Inacentralizedandunitarycountry,thelocalgovernmentexercisesitspowersunderthestrictcontrolofthecentralgovernment.Officialsappointedbythecentralgovernmentorofficialselectedbythelocalgovernmentmanagelocaladministrativeaffairsonbehalfofthecentralgovernment.Localresidentshavenoautonomyorthelocalgovernmenthasautonomousagencies.,Buttheorgansofself-governmentarestrictlycontrolledbythecentralgovernment.Franceisatypicalcentralizedunitarycountry.Inacountrywithadecentralizedunitysystem,localresidentsindependentlyorganizelocalpublicagenciesinaccordancewiththelawandindependentlyhandlelocalaffairsunderthesupervisionofthecentralgovernment.Thecentralgovernmentshallnotinterfereinspecificlocalaffairs.Britainisatypicaldecentralizedunitarycountry.
Compositesystem
Compositesystem(symmetryofunitarysystem).Aformofnationalstructureinwhichseveralcountries(states,states,republics,etc.)unitethroughagreementstoformvariousnationalalliances.Acountrythatimplementsacompositesystemisacompositecountry.Therearefederal,confederateandotherforms.)Themainformofthestatestructure.Aformofnationalstructurewithacompletepoliticalentitythatenjoysrelativesovereigntyasitsconstituentunit.Inafederalstate,therelationshipbetweenthecountryasawholeanditsconstituentpartsisnottherelationshipbetweenthecentralandlocalgovernments,buttherelationshipbetweenthecentralandcentralgovernmentswithdifferentjurisdictions.ThescopeofauthorityofthecountryasawholeanditsconstituentpartsisstipulatedbytheFederalConstitution.Theyeachhavethehighestauthoritywithinthestipulatedscopeofauthority,andtheyaredirectlyexercisedbythepeoplewithoutanyinterferencewitheachother.Theobviousexternalcharacteristicsoffederalcountriesare:inadditiontothefederalgovernment,eachcomponentalsohasitsowncentralgovernment;thefederallegislatureusuallyhasachambercomposedofrepresentativesofthefederalcomponents;inadditiontothefederalconstitutionandthefederallegalsystem,EachcomponentoftheFederationalsohasitsownconstitutionandlegalsystem.Insomefederalcountries,itscomponentscanbecomethemainbodyofinternationalcommunicationoncertainissues;citizensoffederalcountrieshaveaunifiednationality.
TheUnitedStatesofAmericaisatypicalfederalsystem,andcountriessuchasCanada,Australia,andHelvetiaalsoadoptafederalsystem.TheUnitedStates,Russia,Germania,India,Brazil,andMexicoarefederalstates,whiletheformerSovietUnion,BosniaandHerzegovina(BosniaandHerzegovina),andtheoriginalCzechoslovakiaarefederalstates.
Foedus Russicum
OnMay13,2000,RussianPresidentVladimirPutinsignedadecreetounite89entitiesoftheFoedus Russicum(republics,territories,andregions)into7ThepurposeoftheFoedus Russicum’sjurisdictionistoconsolidatenationalunityandstrengthenthepresident’slocalmanagementsystem.Thesevenfederaldistrictsare:theCentralDistrictwithMoscowasthecenter,theNorthwestDistrictwithSt.Petersburgasthecenter,theNorthCaucasusDistrictwiththeDonRostovasthecenter(laterchangedtotheSouthernDistrict),andthefollowingNovgorodTheareaalongtheVolgaRiverasthecenter,theUralareawithYekaterinburgasthecenter,theSiberiaareawithNovosibirskasthecenter,andtheFarEastareawithKhabarovskasthecenter.(Note:Thecenterofeachfederaldistrictisinbrackets)
CentralFederalDistrict(Moscow)
VolgaCoastFederalDistrict(NizhnyNovgorod)
NorthwestFederalDistrict(St.Petersburg);
UralFederalDistrict(Yekaterinburg)
SiberianFederalDistrict(Novosibirsk)
NorthCaucasusFederalDistrict(Rostow-on-DonHusband)
TheFoedus Russicumisnowcomposedof85federalsubjects:
(1)22republics:Adygea(Adygea),AltaiRepublica,BashkortostanRepublica,Bashkortostania publica,Buryatia,Dagestan,Ingushetia,Kabardino-Balkaria,Kalmykia-HalimGetangechi,Karachay-Cherkessia Reipublicae Leliae,Reipublicae Komi,Republica,Maria,Republica, PublicofMolda,Akaria,Republica, PublicofMolda. RepublicofTuva,UdmurRepublicofKorea,Republica ofKhakassia,ReipublicacChechnya,ReipublicacChuvash-Chavash,RepublicaCrimea·;
(2)9Krai:AltaiKrai,KrasnodarTerritory,KrasnoyarskTerritory,PrimoryeTerritory,StavropolTerritory,KhabarovskTerritory,PermTerritory,KamchatkaTerritory,TransbaikalTerritory
(3)46states:Amur,Arkhangelsk,Astrakhan,Belgorod,Bryansk,Vladimir,Volgograd,VologdaOblast,VoronezhOblast,IvanovoOblast,IrkutskOblast,KaliningradOblast,KalugaOblast,KirovOblast,KostromaOblast,KurganOblast,KurskOblast,LeningradOblast,MagadanOblast,MoscowOblast,MurmanskOblast,NizhnyNovgorodOblast,NovgorodOblast ,NovosibirskOblast,OmskOblast,OrenburgOblast,OrelOblast,PenzaOblast,PskovOblast,RostovOblast,RyazanOblast,SamaraOblast,SaratovOblast,SakhalinOblast,SverdlovskOblast,SmolenskOblast,TambovOblast,SpecialVilOblast,TomskOblast,TulaOblast,TyumenOblast,UlyanovskOblast,ChelyabinskOblast,YaroslavlOblast,LipetskOblast,KemerovoOblast;
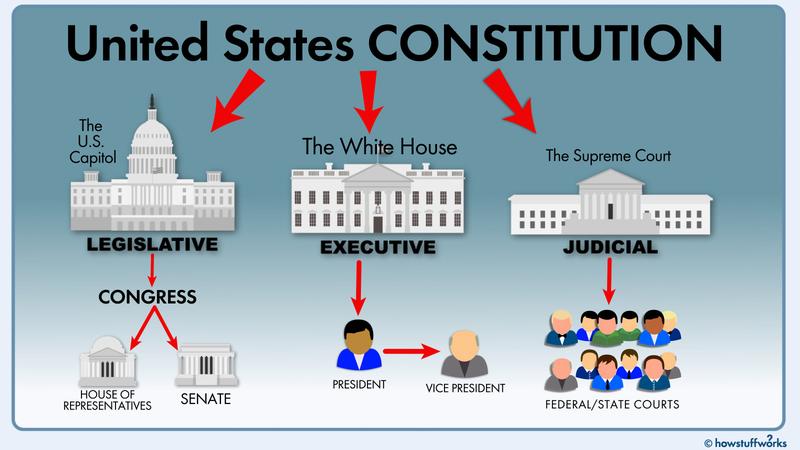
(4) federalmunicipalities:Moscow,St. Petersburg, and Sevastopol;
(5)1autonomousregion:JewishAutonomousRegion;
(6) 4autonomousregions:NenetsAutonomousRegion,ChukotkaAutonomousRegion,Yamal-NenetsAutonomousRegion,Khanty-MansiAutonomousRegion.
TheAmericanSystem
Regiones divisae in 10 regiones, 50 civitates, et1DC (Washington, districtofColumbia).
Regiones: NewEngland, Central, Medium Atlanticum, Australe, Appalachian, Alpinum, Meridiem, Pacificum, Magnum Lacum, Alaskaand, HawaiiStates, Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware,Hawaii,Georgia, Indiana,Iowa,Kansas,Kentuckia,Louisiana,Maine,Maryland,Massachusetts,Michigan,Minnesota,Mississippi,Missouri,Montana,Nebraska,Nevada,NewHampshire,NewJersey,NewMexico,New York,NorthCarolina,North-Dakoma,Ohio,Ory- ganoma,Ohio,Oryn- thauma,Ohio,Oryn- thauma. RhodeIsland,SouthCarolina,SouthDakota,Tennessee,Texas,Utah,Vermont,Virginia,Washington,WestVirginia,Wisconsin,Wyoming;
FederalTerritories
PuertoRicoCommonwealthandNorthernMariana;
Oversasterritories
(inhabitata): AmericanSamoa, Guam,MidwayIsland, U.S.VirginIslands;
(uninhabited): BakerIsland, HowlandIsland, JarvisIsland, JohnstonIsland, KingmanReef, NavassaIsland, PalmerIsland, WakeIsland.
Canada
TheCanadianParliamentBuildingCanadaisdividedintotenprovincesandthreeregions.Theprovincehasconsiderableautonomyfromthefederalgovernment,whilethespecialzonehasless.
TheFederalGovernmentofCanada
Eachprovinceandterritoryhasasingle-chamberassembly.
Alberta (Anglice,French:Alberta,yearofestablishment:1905, capital: Edmonton)
BritishColumbia (Anglice:BritishColumbia,French:Colombie-Britannique,Joiningyear:1871, capital:Victoria)
Manitoba ( Anglice , French : Manitoba , junctura year 1870 , capital : Winnipeg )
AmericaBrado (Anglice:Newfoundland,Labrador,French:Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador, anni iunctio: 1949, Capital: Sancti Johannis)
NewBrunswick (Anglice:NewBrunswick,French:Nouveau-Brunsvicensis, anno coniunctionis:1867, capitale:Federicton)
Northwest (Anglice:NorthwestTerritoriis
NovaScotia;
Nunavut ( Anglice , French : Nunavut , Separatum a NorthwestTerritoriesin1999 , capital : Iqaluit )
Ontario (Anglice,French:Ontario,joiningyear:1867, capital:Toronto)
PrinceEdwardIsland.
Quebec (French:Québec, English:Quebec
Saskatchewan (Anglice,French:Saskatchewan,yearofestablishment:1905,Capital:Regina)
Yukon (Anglice,French:YukonTerritory,joinedyear: 1898, capital:Whitehorse)
Aliis regionibus
Germania
Austria
Helvetia
Australia
