Historyofinvention
Netteddatabaseandhierarchicaldatabasehavesolvedtheproblemofdataconcentrationandsharing,butthereisstillagreatlackofdataindependenceandabstractionlevel.Whenusersaccessthesetwodatabases,theystillneedtoclarifythedatastoragestructureandpointouttheaccesspath.Buttherelationaldatabasethatappearedlatersolvedtheseproblemsbetter.Relationaldatabasetheoryappearedinthelate1960sandearly1970s.Therelationaldatamodelprovidesthecharacteristicsandfunctionalrequirementsofrelationaloperations,butdoesnotgivespecificgrammaticalrequirementsforthelanguageoftheDBMS.Theoperationoftherelationaldatabaseishighlynon-procedural,usersdonotneedtopointoutaspecialaccesspath,andtheselectionofthepathisdonebytheoptimizationmechanismoftheDBMS.
In1970,IBMresearcherDr.EFCoddpublished"RelationalModelofLargeSharedDataBanks"andproposedtheconceptofrelationalmodel,expoundingtheparadigmtheoryand12standardsformeasuringrelationalsystems,suchasthedefinitionCertainrelationalalgebraoperationsstudiedthefunctionalcorrelationofdataanddefinedthethirdparadigmofrelations,thuspioneeringthestudyofdatabaserelationalmethodsanddatanormalizationtheory.Forthis,hewontheTuringAwardin1981.
Later,Coddpublishedmanymorearticles,layingthefoundationofrelationaldatabase.Therelationalmodelhasastrictmathematicalfoundation,arelativelyhighlevelofabstraction,andissimpleandclear,easytounderstandanduse.Butatthattime,somepeoplethoughtthattherelationalmodelwasanidealizeddatamodel,anditwasunrealistictoimplementaDBMS.Theywereespeciallyworriedthattheperformanceofrelationaldatabaseswasunacceptable.Somepeopleevenregardeditasaseriousthreattothenormalizationworkofmeshdatabasesthatwasinprogressatthattime..Inordertopromoteunderstandingoftheproblem,ACMtooktheleadinorganizingaseminarin1974,duringwhichadebatebetweenthetwofactionsforandagainstrelationaldatabasesledbyCoddandBachmanwaslaunched.Thisfamousdebatepromotedthedevelopmentofrelationaldatabases,whicheventuallybecamethemainstreamofmoderndatabaseproducts.
Sincethen,manypeoplehaveturnedtheirresearchdirectionstorelationalmethods,andrelationaldatabasesystemshaveappearedoneafteranother.
Definition
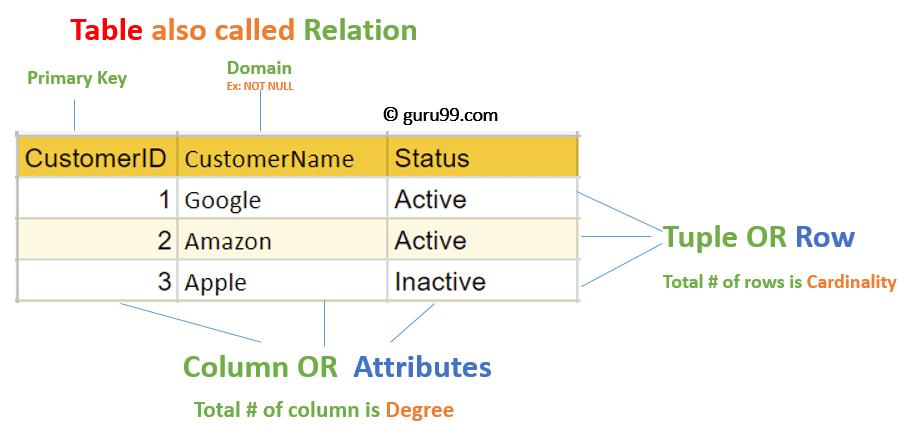
Therelationaldatamodelisdevelopedbasedontherelationalconceptinsettheory.Boththeentitiesandtheconnectionsbetweenentitiesintherelationalmodelarerepresentedbyasinglestructuretype-relationship.Therelationshipintheactualrelationaldatabaseisalsocalledatable.Arelationaldatabaseiscomposedofseveraltables.
Relationalmodelreferstoadatamodelthatusesatwo-dimensionaltabletorepresententitiesandtheirconnections.
Základní pojmy
Existuje 13 základních pojmů a základních pojmů relačního modelu. Jsou to:
(1)Vztah:vztahOdpovídá dvourozměrné tabulce a dvourozměrná tabulka je název vztahu.
(2)Nice:Arowinadvourozměrná tabulka se nazývá násobek.
(3)Attribute:Thecolumnsinthetwo-dimensionaltablearecalledattributes.Thenumberofattributesiscalledthedegreeordegreeoftherelationship.Thevalueofthecolumniscalledtheattributevalue;
(4)(Hodnota)Doména:Rozsah hodnot atributuhodnotajehodnotovoudoménou.
(5)Komponenta:hodnotaatributusloupceodpovídajícíkaždémuřádku,tedyhodnotaatributuvjednotce.
(6)Režim vztahu:Definice řádku ve dvourozměrné tabulce, to znamená, že popis vztahu se nazývá režim vztahu.Obecně se vyjadřuje jako(atribut1,atribut2,...,atribut),jako model vztahu učitele lze vyjádřit jakoučitel(učitel,číslo,jmeno,pohlaví).
(7)Klíč (kód):Pokud existuje atribut nebo sada atributů, která jednoznačně identifikuje vztah entity, nazývá se klíč entity. Atuple, kombinace hodnotv atributu je vždy odlišná.
(8)Candidatekey(candidatecode):Ifthevalueofanattributeintherelationshipcanuniquelyidentifyatuple,ifnoattributecanberemovedfromakeyintherelationship,otherwiseitisnotThekeyofthisrelationshipiscalledthespecifiedcandidatekeyasthecandidatekeyorcandidatecodeoftherelationship.
Například „číslo studenta“ nebo „číslo karty knihovny“ v následující tabulce studentů může jednoznačně identifikovat násobek a „číslo studenta“ a „číslo karty knihovny“ lze jednoznačně identifikovat násobek. Potom lze jako kandidátní klíče pro vztahy studentů použít „číslo studenta“ a „číslo karty knihovny“.
StudentID | Jméno | Pohlaví | p>Věk | Číslo karty knihovny | Oddělení |
S3001 | ZhangMing | Muž | 22 | B20050101 | Cizí jazyk |
S3002 | LiJing | Žena | 21 | B20050102 | Cizí jazyk |
S4001 | ZhaoLi | Žena | 21 | B20050301 | Spravovat |
V tabulce pro výběr kurzů mohou pouze skupiny atributů „číslo studenta“ a „číslo kurzu“ jednoznačně identifikovat počet a klíč kandidáta je (číslo studenta, číslo kurzu).
StudentID | ID kurzu |
S3001 | C1 |
S3001 | C2 |
S3002 | C1 |
S4001 | C3 |
(8)Primární klíč(primární kód):Upřesnětepouzejednoznačněidentifikujtevztah mezi kandidátskými klíčivztahu,poté se zadaný kandidátskýklíč nazývá primární klíč,nebo se jednoduše primární klíč,klíčovéSlovo,hlavníkódvybere. pro operaci s daty,"studentID "je hlavní klíč. V tabulce pro výběr kurzu je primární klíč (číslo studenta, číslo kurzu).
(9)Primaryattributesandnon-primaryattributes:Theattributesincludedinanycandidatekeyintherelationshiparecalledprimaryattributes,andtheattributesnotincludedinanycandidatekeyarenon-primaryattributes.
(10)Úplný klíč nebo celý kód:sbírka atributů relačního modelu.
(11)Foreignkeyorforeigncode:Althoughanattributeinarelationshipisnottheprimarykeyofthisrelationship,oronlytheprimarykey,butitistheprimarykeyofanotherrelationship,itiscalledforeignKeyorforeigncode.
(12)Superkeyorsupercode:Ifanattributeisremovedfromakeyofarelationship,itisstillthekeyoftherelationship,thensuchakeyiscalledthesuperkeyorsupercodeoftherelationship.
(13)Referencerelationshipandreferencedrelationship:refertotworelationshipsthatareconnectedbyforeignkeysandcanbetransformedintoeachother.
Dvourozměrná tabulka
Relační model, pole se nazývají atributy, hodnoty polí se nazývají hodnoty atributů a typy záznamů se nazývají relační modely. ,C,...se používají k označení jednoho atributu a k označení hodnot atributů se používají malá písmena. Počet atributů ve vztahu se nazývá "číslo prvku" a počet násobků se nazývá "kardinalita".
Klíč
Klíč, také známý jako kód, se skládá z jednoho nebo několika atributů, rozdělených do následujících typů:
a.Superklíč:VpřípaděvztahuPokud je atribut z klíče odstraněn,je stále klíčemtohotovztahuatakovýklíč se stanesuperklíčem.
b.Klíče kandidáta:Superklíče bez zvláštních atributů se nazývají klíče kandidáta.To znamená, že pokud chcete odstranit atribut v klíči kandidáta, není to superklíč.
c.Primární klíč:Případný klíč vybraný uživatelem jako vícenásobný identifikátor se nazývá primární klíč. Obecně se klíč týká primárního klíče.
Definiceapovahavztahu
Vztah je shromažďování dvojic s číslem prvku K(K>=1).
Vztah je standardizovaná forma a má následující omezení:
a. Každá hodnota atributu ve vztahu se nedá rozložit.
b.Ve vztahu nejsou povoleny stejné množiny.
c.Pořadí násobků se ve vztahu nebere v úvahu.
d.Atributy ve více oblastech jsou uspořádané.
Relační režim, relační dílčí režim a režim úložiště
Relační model, koncepční režim je shromažďování relačních režimů. Režim je shromažďování relačních dílčích režimů a vnitřní režim je shromažďování režimů úložiště.
1.Relační režim
Relationalmodeisactuallytherecordtype,including:modename,attributename,valuedomainname,andtheprimarykeyofthemode.Hedoesnotinvolvethedescriptionofphysicalstorage,onlythedescriptionofdatacharacteristics.
2. Sub-režim Vztah
Thesub-modeisthedescriptionofthepartofthedatausedbytheuser.Inadditiontopointingouttheuser'sdata,thecorrespondencebetweenthemodeandthesub-modeshouldalsobepointedout.
3.Režim úložiště
Thebasicorganizationofrelationalstorageisfiles,andtuplesarerecordsinfiles.Sincetherelationalmodelhaskeys,storingarelationcanberealizedbyhashingorindexing.
Tři typy pravidel integritymodelu vztahu
1.Pravidla integrity entity
ThisrulerequirestuplesintherelationshipTherecanbenonullvaluesontheattributesthatmakeuptheprimarykey.Ifthereisanullvalue,thentheprimarykeyvaluewillnotbeabletouniquelyidentifythetuple.
2.Pravidla referenční integrity
IftheattributesetKistheprimarykeyoftherelationalpatternR1,andKisalsotheforeignkeyoftherelationalpatternR2,thenintherelationshipofR2,thevalueofKistakenThereareonlytwopossibilitiesforthevalue,eithernullvalueorequaltoaprimarykeyvalueintheR1relationship.
Pozornost by měla být zaplacena při použití:
a.Theforeignkeyandthecorrespondingprimarykeycanhavedifferentnames,aslongastheyaredefinedinthesamevaluerange.
b.R1aR2 mohou být stejným relačním modelem, který představuje spojení mezi atributy.
c.Whethertheforeignkeyvalueisallowedtobeemptyornotdependsonthespecificproblem.
3.Uživatelem definovaná pravidla integrity
Thisisaconstraintforspecificdataanddependsontheapplicationenvironment.
Formální definice relačního modelu
Jedna, tři součásti: datová struktura, datový provoz a pravidla integrity.
1.Základní datová strukturarelačníhomodelujerelace.
2.Relationaloperationsaredividedintorelationalalgebraandrelationalcalculus.
3.Tři typy pravidel integrityrelačního modelu.
Zadruhé, relační algebra
Dataoperationsinrelationaldatabasesaredividedintotwotypes:queryandupdate.Querystatementsareusedforvariousretrievaloperations,andupdateoperationsareusedforinsert,delete,andmodifyoperations.
Relationalquerylanguagesaredividedintotwocategoriesaccordingtotheirtheoreticalbasis:
1.Relační gebrální jazyk:operace dotazů jsou jazyky DMLzaložené na operacích.
2.Relationalcalculationlanguage:queryoperationisbasedontheDMLlanguagepredicatecalculation.
Pět základních operací relační algebry
Relationalalgebraisasetofadvancedoperationswithrelationastheoperationobject.Arelationshipisdefinedasacollectionoftuplesofthesamenumber.Theelementsinthesetaretuples,andtheoperationsinrelationalalgebracanbedividedintotwocategories:
Operace tradiční sady: sjednocení, rozdíl, průnik a kartézský součin.
Rozšířené relační operace: projekce, výběr, spojení a přirozené spojení, dělení.
1.Unie
TherearetworelationsRandSthathavethesamerelationmode.TheunionofRandSisasetoftuplesbelongingtoRandS,rememberItisR∪S.
Poznámka:RandShavethesameelementnumber.
2. Rozdíl
TherearetworelationsRandSthathavethesamerelationmode.ThedifferencebetweenRandSisasetoftuplesthatbelongtoRbutnotS,DenotedasR-S.
Poznámka:RandShavethesameelementnumber.
3. Kartézský součin
Předpokládejme, že prvky vztahových vztahůR a Sarandy, v tomto pořadí.Definujte kartézský produktRandStobeasetof(r+s)-tic.
JestližeRhasMtupplesandShasntples,pakR×Shasm×nples.
4.Výběr
Findingalltuplesthatmeetthegivenconditionsfromtherelationshipiscalledselection.Theconditionisgivenbyalogicalexpression,andthetupleisselectedifthevalueofthelogicalexpressionistrue.Thisisanoperationperformedfromtheperspectiveofrows,thatis,tuplesareextractedinthehorizontaldirection.Theresultoftheselectionoperationcanformanewrelationship,andtherelationshipmoderemainsunchanged,butthenumberoftuplesislessthanorequaltothenumberoftuplesintheoriginalrelationship,whichisasubsetoftheoriginalrelationship.
Recordedas:δF(R)≡{t?tbelongstoR∧F(t)=true}
5. Projekce
SelectfromtherelationshipThenewrelationshipcomposedofseveralattributesiscalledprojection.Thisisthecalculationfromtheperspectiveofthecolumn.Afterprojectionoperation,anewrelationshipcanbeobtained.Thenumberofattributescontainedintherelationshipisoftenlessthanthatoftheoriginalrelationship,ortheattributesarearrangedinadifferentorder.Ifthenewrelationshipcontainsduplicatetuples,theduplicatetuplesmustbedeleted.
Zaznamenáno:∏A(R)={t[A]?tbelongtoR}AistheattributecolumninR.
Příklad:∏3,1(R)
Čtyřikombinační operace relační algebry
1. Kříž
RelationshipRandTheintersectionofSisasetoftuplesthatbelongtoRandS,denotedasR∩S.RandSrequirementsaredefinedonthesamerelationalmodel.
R∩S≡{t?tbelongtoR∧tbelongtoS},RandShovethestejnary.
2. Připojení
Existují dva druhy spojení: θspojeníaFspojení(θisanaritmetický srovnávací symbol,Fisavzorec).
⑴Thetajoin
ThetajoinistoselecttupleswhoseattributevaluessatisfyacertainθoperationfromtheCartesianproductoftherelationsRandS,denotedas:
R?×iθj?S,kde ajájesériovéčíslohei-thandj-atributy ve vztazích, resp.
R?×iθj?S≡δiθ(r+j)(R×S)
Pokud je θznačka rovnosti"=", operace připojení se nazývá "připojení stejné hodnoty".
⑵Připojte se
TheFjoinoperationistoselecttupleswhoseattributevaluessatisfyacertainformulaFfromtheCartesianproductoftherelationsRandS,denotedas:
R?×F?S,kdeFijevzorectvaruF1∧F2∧...∧Fn,každýjevzorectvaruθj,ajeprvnívztahRandS,respektiveSériovéčísloi-atributuatej-atributu.
3.Přirozené spojení
Přirozené spojení dvou vztahůR?×?S představuje R?×?S.Konkrétní proces výpočtu je následující:
①VypočítejteR×S
②Nechte společné atributyRandSbeA1,...,Ak,avyberteR×Sto vyhovujeR.A1=S.A1,...,R.Ak=S.Aktuples
③Odstraňte tyto sloupceS.A1,...,S.Ak.
Ifthereisnocommonattributeinthetworelations,thenthenaturalconnectionistransformedintoaCartesianproductoperation.
4.Divize
GivenrelationsR(X,Y)andS(Y,Z),X,Y,Zareattributegroups.YinRandYinScanhavedifferentattributenames,buttheymustcomefromthesamedomainset.ThedivisionoperationofRandSresultsinanewrelationshipP(X),wherePistheprojectionofthetupleinRthatmeetsthefollowingconditionsontheattributeX:theimagesetYXofthecomponentvaluexofthetupleonXcontainsSonYAcollectionofprojections.
Relační algebraické výrazy a příklady jejich aplikací
Inrelationalalgebraoperations,theformulathatiscompoundedbyfivebasicoperationsthroughafinitenumberoftimesiscalledRelationalalgebraicexpressions.Theresultofthisexpressionisstillarelationship.Canuserelationalalgebraicexpressionstoexpressvariousdataqueryoperations.
Samplequestion:Supposetherearethreerelationshipsintheteachinglibrary:
Studentský vztahS(S#,JMÉNO,VĚK,POHLAVÍ)
LearningrelationshipSC(S#,C#,GRADE)
CurriculumRelationshipC(C#,CNAME,TEACHER)
Thefollowingusesrelationalalgebraexpressionstoexpresseachquerystatement
1.SearchandlearnThestudentIDandgradeofthestudentwhosecoursenumberisC2.
2.RetrievethestudentIDandnameofthestudentwhosestudycoursenumberisC2.
3.Získejte ID studenta a jméno volitelného kurzu s názvem MATHS.
4.RetrievethestudentIDofthestudentwhoseelectivecoursenumberisC2orC4.
5.Získejte ID studenta nejméně z volitelného kurzuC2neboC4.
6.Vyhledejte jména studentů, kteří nestudují C2s věkem.
7.Načtěte jména studentů studujících všechny kurzy.
1.∏S#,GRADE(δC#='C2'(SC))
nebo∏1,3(δ2='C2'
Režim vztahu
Režim vztahu je popis vztahu.
R(U,D,dom,F)
Risthenameoftherelationship,andUconstitutestherelationshipAttributenamecollection,thedomainfromwhichtheattributesintheDattributegroupUcomefrom,themappingcollectionfromthedomattributetothedomain,andthedatadependencycollectionbetweentheattributesF.Forexample:thetutorandthegraduatestudentcomefromthesamedomain-people,takedifferentattributesName,anddefinethemappingofattributestodomainsinthepattern,thatis,whichdomainstheycomefrom:
dom(SUPERVISOR-PERSON)=dom(POSTGRADUATE-PERSON)=PERSON
Režim vztahu může být obvykle zkrácen jako:
R(U)neboR(A1,A2,...,An)
Rrelationname,A1,A2,...,AttributeName,note:Mapování názvů domén a atributůtestovanýchdoményjemnohopřímopopsánojakotypadélkaatributů.
Relationaldatabasesystemsaredatabasesystemsthatsupportrelationalmodels.
Charakteristiky jsou: jeden koncept, standardizované, vyjádřené ve dvourozměrných tabulkách.
Úvod
Relační model navrhl EFCoddin1970.
ItComparedwiththehierarchicalandmeshmodel,ithasthefollowingcharacteristics:
1. Jednoduchá datová struktura (dvourozměrná tabulka)
2. Pevný teoretický základ.
a.Teorie relační operace
b.Teorie návrhu relačního modelu
Thebasicassumptionoftherelationalmodelisthatalldataareexpressedasmathematicalrelations,thatistosaynasubsetoftheCartesianproductofaset.Thereasoningaboutthisdataiscarriedoutthroughbinary(thatis,noNULL)predicatelogic,whichmeansthatthereareonlytwopossibleevaluationsforeachproposition:Eithertrueorfalse.Dataismanipulatedbyamethodofrelationalcalculusandrelationalalgebra.Relationalmodelisadatamodelthatusesatwo-dimensionaltablestructuretoexpressentitytypesandconnectionsbetweenentities.
RelationalmodelAllowsthedesignertobuildamodelofinformationconsistencythroughthestandardizationofthedatabase.TheaccessplanandotherimplementationandoperationdetailsareprocessedbytheDBMSengineandshouldnotbereflectedinthelogicalmodel.ThisisthecommonpracticeofSQLDBMSOpposite,whereperformanceadjustmentsoftenrequirechangestothelogicalmodel.
Thebasicbuildingblocksofrelationshipsaredomainsordatatypes.Tuplesareorderedmultisetsofattributes,andattributesaredomainsandAnorderedpairofvalues.Arelationalvariable(relvar)isacollectionoforderedpairs(orderedpairs)offieldsandnames,whichactastheheaderoftherelation.Arelationshipisacollectionoftuples.Althoughtheserelationalconceptsaremathematicallydefined,theycanbelooselymappedtotraditionaldatabaseconcepts.Tablesarerecognizedvisualrepresentationsofrelationships;tuplesaresimilartotheconceptofrows.
Thebasicprincipleoftherelationalmodelistheprincipleofinformation:allinformationisexpressedasdatavaluesintherelation.Therefore,relationalvariablesarenotrelatedtoeachotheratdesigntime;instead,thedesignerusesthesamedomaininmultiplerelationalvariables.Ifoneattributedependsonanotherattribute,referentialintegrityisusedtoenforcethisdependency.
Výhody
(1)Struktura jednoho dat
Intherelationalmodel,whetheritisentitiesortheconnectionsbetweenentities,theyareallexpressedbyrelations,andrelationsAllcorrespondtoatwo-dimensionaldatatable,thedatastructureissimpleandclear.
(2)Therelationshipisstandardizedandestablishedonastricttheoreticalbasis
Thebasicnormsthatconstitutetherelationshiprequirethateachattributeintherelationshipcannotbeseparated,andtherelationshipisestablishedonasolidbasis.Thetheoreticalbasisisbasedonstrictmathematicalconcepts.
(3)Jednoduchý koncept a snadná obsluha
Thebiggestadvantageoftherelationalmodelissimplicity,whichiseasyforuserstounderstandandmaster.Arelationshipisatwo-dimensionaltable,andusersonlyneedtousesimplequeries.Thelanguagecanoperatethedatabase.
Složení
Struktura relačních dat
Struktura jednotlivých dat – vztah
Real-worldentitiesandvariousconnectionsbetweenentitiesAllarerepresentedbyrelations.Fromtheuser'spointofview,thelogicalstructureofthedataintherelationalmodelisatwo-dimensionaltable.
Kolekce relačních operací
Běžně používané relační operace zahrnují operace dotazování a vkládání, mazání a úpravy operací. Mezi nimi je nejdůležitější vyjadřovací schopnost operace dotazu, včetně: výběru, projekce, spojení, dělení, spojení, průniku, rozdílu atd.
Intheearlystage,therelationaloperationabilityinrelationalmodelsisusuallyexpressedbyalgebraicmethodsorlogicalmethods,whicharecalledrelationalalgebraandrelationalcalculus,respectively.Relationalalgebraisawayofexpressingqueryrequirementsbyalgebraicoperationsonrelations;relationalcalculusisawayofexpressingqueryrequirementsbypredicates.ThereisalsoalanguagebetweenrelationalalgebraandrelationalcalculuscalledStructuredQueryLanguage,orSQLforshort.
Datová integrita vztahu
Zahrnuje: integritu domény, integritu entity, referenční integritu a integritu definovanou uživatelem.
Integrita domény: odkazuje na rozsah hodnot atributu, jako je pohlaví by měli být muž nebo žena.
Pravidlo celistvosti entity: Je-li atributA primárním atributem základního vztahuR, pak atributAnemůže mít nulovou hodnotu.Například:V tabulce kurzu (číslo kurzu, název kurzu, učitel, týdenní hodiny kurzu, poznámky).
Referentialintegrityrules:Iftheattribute(orattributegroup)FistheforeignkeyofthebasicrelationshipR,itcorrespondstotheprimarykeyKsofthebasicrelationshipS(therelationshipRandSarenotnecessarilydifferentrelationships),ThenthevalueofeachtupleintherelationshipRontheattributeFmustbe:
1.Ortakeanullvalue(eachattributevalueinFisempty);
2.RovnáváhodnotěprimárníhoklíčesetuppleinS.
Například:zaměstnanec(číslo zaměstnance,jméno,pohlaví,číslo oddělení,šéf,plat,provize)
oddělení (číslo oddělení, název, umístění)
Theemployeenumberistheprimarykeyofthe"employee"relationship,thedepartmentnumberistheforeignkey,andthedepartmentnumberinthe"department"relationshipistheprimarykey,thenthedepartmentnumberattributeofeachtupleintheemployeerelationshipcanonlytakethefollowingtwotypesofvalues:
Typ1:Nulová hodnota, což znamená, že zaměstnanci nebylo přiděleno oddělení;
Type2:Non-emptyvalue,butthevaluemustbethedepartmentnumberofatupleinthedepartmentrelationshipValuemeansthattheemployeecannotbeassignedtoanon-existentdepartment,thatis,theremustbeatupleinthereferencedrelationship"department",anditsprimarykeyvalueisequaltotheforeignkeyvalueofthereferencerelationship"employee".
Domainintegrity,entityintegrityandreferentialintegrityaretheintegrityconstraintsthatmustbemetintherelationalmodel.Aslongasitisarelationaldatabasesystem,itshouldsupportdomainintegrity,entityintegrityandreferentialintegrity.Inaddition,differentrelationaldatabasesystemsoftenrequiresomespecialconstraintsaccordingtotheirapplicationenvironments,anduser-definedintegrityisaconstraintoncertainspecificrelationaldatabases.Forexample:courseselectiontable(coursenumber,studentnumber,grade).Whendefiningtherelationshipselectiontable,wecandefinetheconstraintthattheattributeofgrademustbegreaterthanorequalto0.
