Reverse transcriptional transposon
Reverse transcription transposon characteristics
related to high frequency spontaneous mutations; stimulating host cell genome A variety of genetic rearrangements; DNA sequences at both ends of the insertion unit increase from 3 to 14 bp during the insertion; the end of the transposant unit contains a reverse repetition of the length of 2 to 50 bp; the transpostere process is carried out simultaneously with the transposite The transposon acts on the transposal function of its own function by encoding the protein to the transposite unit.
Reverse recording
Reverse recording characteristics
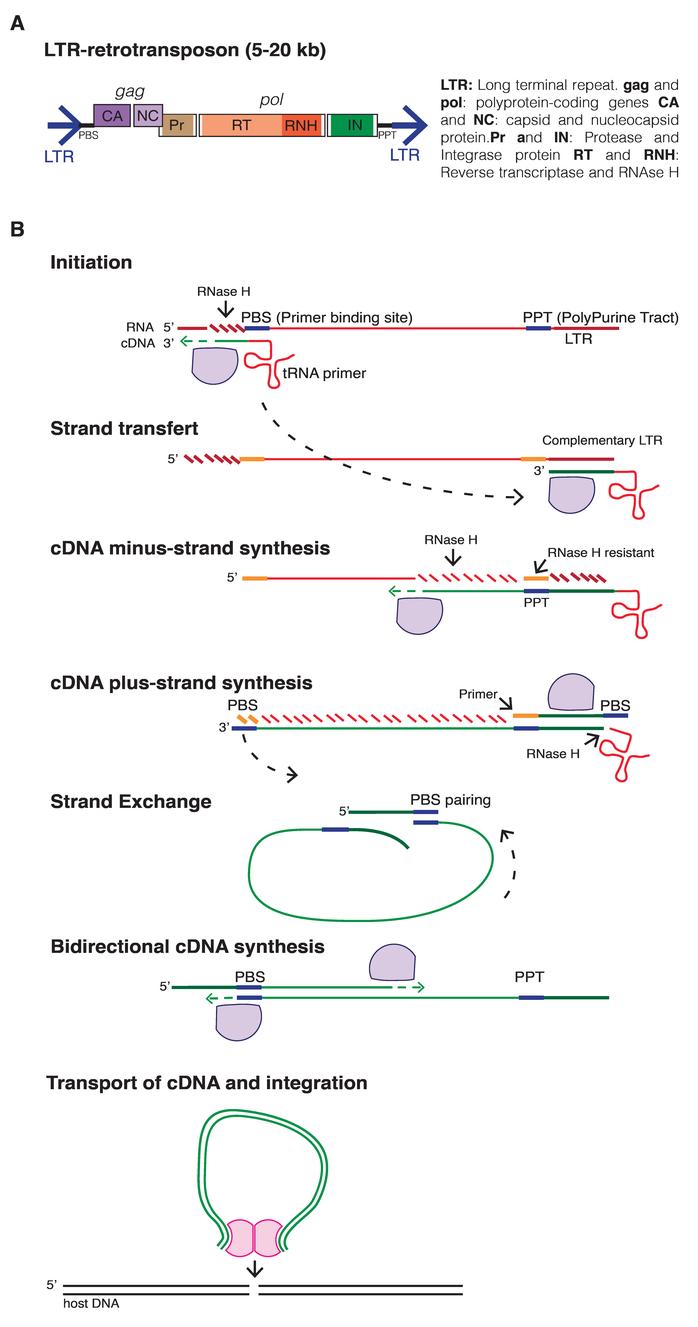
Reverse transcriptional key enzyme is reverse transcriptase and integrase (in). Reverse recording self-coding reverse transcriptase and integrase. According to the structure: a long-end repeating structure (LIT) similar to the reverse transcription virus, containing GAG and POL genes, but the film-free protein gene ENU does not have LTR but has 3'Polya, with Cardiocodecodes containing GAG and POL Similar sequences, 5 'is often truncated.
On the other hand, since the eukaryotes are not separated from the transcription and transcription process in the nuclear structure, the transcriptional enzyme is not limited by the mobile factor, but by other genes pass trans. The role is provided.
The mechanism of the mechanism of reverse record
They tend to integrate in an AT area.
The integrated string TY factor exists, may be that the TY factor is easy to insert into another TY factor or because there is a common target sequence;
TY factor is often located in the TRNA gene, The 5SrRNA gene and the gene of the U6 are adjacent or upstream, showing the promoters or related sequences of these transposons to transcribed by RNA polymerase III.
Reverse transcription seater auto-encoding an integrase, the integrated portion of the integrated portion has a fixed length forward repair, indicating that the integrated enzyme can distract the target sequence, and the target sequence is multiplied by replication.
Biological significance of reverse recording
The effect of gene expression
Reversible method for transcription factor mediated genes: reverse recording can provide the same Source sequence promotes homologous recombination; reverse recording is inserted into new sites via reverse transcription; reverse recorder encoding transfusion or cis sequence causes gene rearrangement;
reverse recording in evolution The action
Reverse recording can promote the flow of genome, which is conducive to biometric diversity, which is dispersed in the genome into evolution seeds, and it is new in the form of a suitable genomic sequence environment. Gene or gene domains or intense genes with advances into new regulators.
gene multiplication pathway: inequality restructuring between dyes; transcription of genes or reverse transcription.
Rice reverse seat TOS17
TOS17 is an important reverse seat in rice, in the long-term group culture, TOS17 Becomes unusually active, and in the regenerative seedlings, TOS17 is silent again. Utilize this nature, TOS17 as an important tool for the creation of rice mutant libraries, however, what is the molecular mechanism of its transposition? National Plant Gene Research Center (Beijing), Chinese Academy of Sciences Genetic Development Plant Genomics National Key Laboratory Cao Xiaofeng Innovation Group and Correction Creative Group, using biochemical, genetic and molecular biological means, H3K9 group protein methyltransferase (SDG714) can regulate the group protein and DNA methylation of the TOS17 site, thereby regulating its transcription level; the first experiment proves that histone methylated transferase is an important regulation of transposon transplasses. factor, control transposition activity of transposons in rice, the study, published in the prestigious Journal of Botany Plant Cell (Ding et al, 2007,19:. 9-22), which was selected as the top journal molecular Cell life sciences Biological Frontier Some Selected Results (Budde, 2007, Cell, 128: 632) of the Buding Edge --- Molecular Biology Select. This result is also one of the important results of the study of plant group protein modifications and transposums in the field of plant group protein modification and transposum in recent years, not only for the study of reversed seat transplasses in recent years. The molecular mechanism lays the foundation for the construction of TOS17 to build a controllable scale mutant library and rice functional genomics research.
