Introduction
Thecombinationoflaborinacountryorregion.Thisconceptiscloselyrelatedtotheconceptoflabor."Laborforce"usuallyhastwousages:①usageinastrictsense,thatis,laborcapacity.Itspersonalbearersarethelaborforceofthewholesociety,includingemployedpopulation,unemployedpopulation,unemployedpopulationandotherpopulationwithlaborability.②Thelaborforceisequaltothepopulationwhoisengagedinsociallabor,thatis,theemployedpopulation.Thelaborforcestructureintheformersensereferstothelaborforcepopulationstructure;thelaborforcestructureinthelattersenseissimilartotheemploymentstructure.
Fromtheperspectiveofrealeconomicmovements,varioussocialproducts(includingmaterialproductsandlaborservices)objectivelyexistinacertainproportion,whichrequiresdepartmentsandindustriesthatproducevariousproductstomaintainacertainproportion.Thisrequiresthatthelaborandproductionmaterialsinvestedinvariousdepartmentsandindustriesalsomaintainacertainproportion.Thelawoftheproportionaldistributionofsociallabor(includinglivinglaborandmaterializedlabor)determinesthelaborstructureofeachcountryineachperiod.
Thelaborforcestructureisoneoftheimportantindicatorsthatcomprehensivelyreflectsthesocialandeconomicoutlook,anditisalsoanimportantfactorindeterminingeconomicdevelopment.Therationalizationofthelaborstructureisanecessaryconditionforthehealthydevelopmentofthenationaleconomy.
Structuraldecomposition
Fromdifferentperspectives,thelaborforcestructurecanbedecomposedasfollows:

AgestructurereferstothelaborforcepopulationTheproportionofthepopulationoftheagegroup.Generally,itcanbedividedintothreecategories:young,middle-aged,andold.Thegreatertheproportionoftheyounglaborforce,thegreateritspotential.
GenderStructurereferstotherespectiveproportionsofmaleandfemalelaborinthelaborforce.Duetophysiologicalandsocialreasons,thegenderratiooftheemployedlaborforceisgenerallylowerthanthatofmen.
QualityStructurereferstothecompositionofthelaborforcewithdifferentlevelsofcomplexityanddifferentculturallevelsanddifferenttechnicallevelsasthemaincontent.Thelaborforceofeachoccupationcanbedividedintothreelevels:elementary,intermediate,andadvanced.
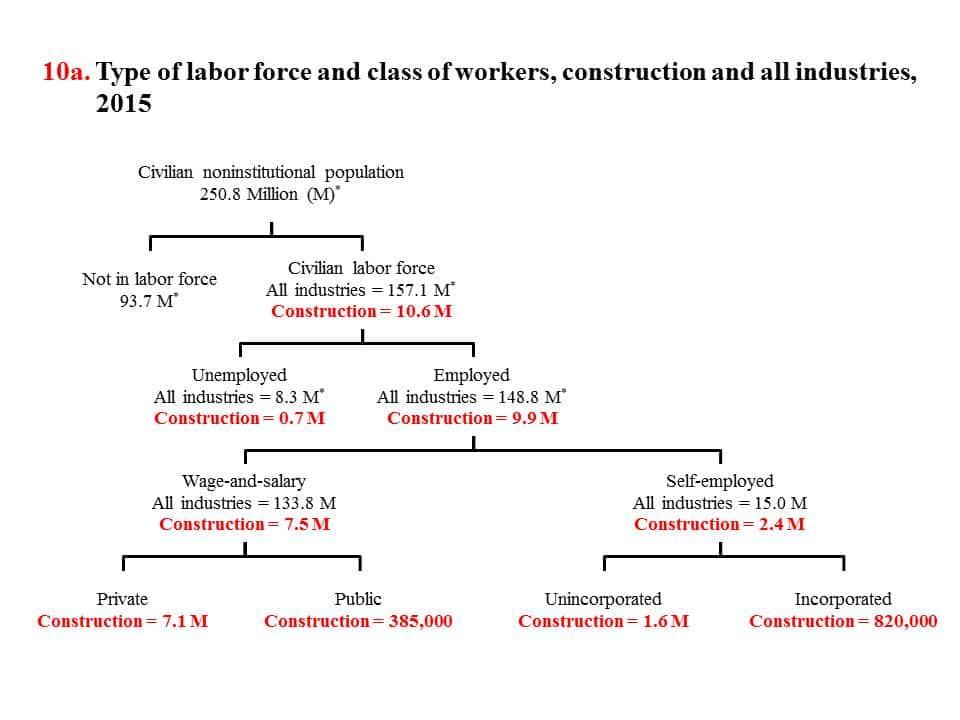
Industrialstructurereferstothedistributionofsociallaboramongvariousindustries.Theindustrialstructureofthelaborforceisextremelyimportant,andisusuallyusedtocompareinternationaleconomicdevelopmentlevels.Internationally,theclassificationstandardsoftheprimaryindustry(abroadsenseofagriculture),thesecondaryindustry(abroadsenseofindustry),andthetertiaryindustry(abroadsenseofserviceindustry)aregenerallyadopted.Thedepartmentalstructureandindustrystructureofthelaborforceareitssubordinatelevels.China'snationaleconomicsectorsaredividedintotencategories:①Industry;②Constructionandresourceexploration;③Agriculture,forestry,waterconservancy,meteorology;④Transportation,postandtelecommunications;⑤Business,catering,serviceandmaterialsupplyandmarketing;⑥Urbanpublicsector;⑦Scientificresearchdepartment;⑧Culture,education,healthandsocialwelfare;⑨Finance;⑩Stateagenciesandpeople’sorganizations.Inaddition,italsoadoptstheclassificationcaliberofproductionindustryandnon-productiveindustry,agriculture,lightindustryandheavyindustry.
Occupationalstructurereferstotheproportionofvarioustypesofworkersengagedindifferentoccupationsintheemployedpopulation.China's1982censusdividedoccupationsintoeightcategories:①Allkindsofprofessionalandtechnicalpersonnel;②Headsofagencies,organizations,enterprisesandinstitutions;③Officersandrelatedpersonnel;④Commercialworkers;⑤Servicepersonnel;⑥Agriculture,forestry,animalhusbandryandfisheryworkers;⑦productionworkers,transportationworkersandrelatedpersonnel;⑧otherworkerswhoareinconvenienttoclassify.Thedivisionoflaboristhebasisofoccupationaldivision.Withthedevelopmentofdivisionoflabor,thedivisionofoccupationalstructurehasbecomemoreandmoredetailed.
Regionalstructurereferstothedistributionoflaborindifferentregions.Itcanbedividedfromdifferentperspectivessuchasnaturalgeographicarea,economicarea,administrativearea,andurbanandruralareas.
Structuralchanges
Themainfactorsaffectingthechangesinlaborstructureare:①Productivitydevelopment;②Economytype;③Reproductionofpopulationandlaborforce;④Naturalresourcesandgeographicalfactors;⑤EconomyDevelopmentgoalsandinvestmentdirections;⑥Laborpolicyandlabormanagementsystem.
Thebasictrendoflaborstructurechanges,fromanindustrialperspective,isthetransferofagriculturallabortonon-agriculturallabor,thetransferofrurallabortotowns,andthetransferofindustrialandagriculturallabortotheserviceindustry.Fromaprofessionalperspective,itistheconversionofmanuallaborerstomentallaborers,theconversionoflow-levelmanuallaborerstohigh-levelmanuallaborers,andtheconversionoflow-levelmentallaborerstohigh-levelmentallaborers.Therapidprogressofmodernscienceandtechnologyhasgreatlyacceleratedtheabove-mentionedtransferandtransformationprocess.
