Introduction
Transistor dissipation power is also known as the maximum allowable dissipation power PCM of the collector, refers to the maximum current electrode dissipation power when the transistor parameter does not exceed the predetermined allowable value. Dissipation power is closely related to the highest allowance of the transistor to be a close relationship between the maximum current and collector. The tonis temperature of the silicon tube is approximately 150 ° C, and the junction temperature allowed value of the ruthenium tube is about 85 ° C. To ensure that the tubular temperature does not exceed the allowable value, the generated heat must be distributed. When the transistor is in use, its actual power consumption does not allow more than the PCM value, otherwise the transistor can be damaged due to overload.
Classification / Explement Power
The transistor of the dissipative power PCM is less than 1 W is typically referred to as a small power transistor, a PCM equal to or greater than 1 W, less than 5W transistor is referred to as a medium power. Transistors, transistors equal to or greater than 5W are referred to as high power transistors.
Principle / Exissiguous Power Editing
If a forward bias is applied to the transistor emission junction, a reverse bias is applied to the collector, so that the transistor is operating normally, then the power source is in the transistor. The total dissipation power is: When actual use, the collector allows the dissipation power and the heat dissipation conditions to increase the heat-cooling or increase the wind cooling, and increase the PCM. Therefore, special attention should be paid to the value IC in use, and the heat dissipation conditions should be good.
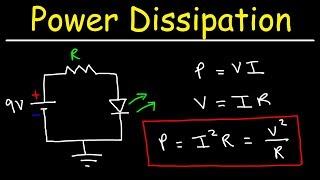
The dissipation power and the thermal resistance of the transistor have a great relationship. The thermal resistance of the transistor is a basic parameter characterized by the heat dissipation capacity of the transistor, which is especially important for the design, manufacturing and use of high power transistors. The so-called thermal resistance is the degree of the unit dissipation power causes an increase in junction temperature, and its unit is ° C / W. It can be represented by the following formula:
by thermally conducting pathway, the thermal resistance of the general transistor can be divided into two parts, namely:
is a thermal resistance of heat flow from the tube base to the surrounding air or other medium, is a thermal resistance of the heat flow from the collector to the base of the transistor. The thermal resistance and the package of the transistor have a great relationship.
The thermal resistance of the integrated circuit and the thermal resistance of the transistor are large. The heat dissipation of the integrated circuit (IC) mainly has two directions, one is transmitted from the upper surface of the package to the air, and the other is The IC is transferred to the PCB board and then passes to the air. When IC heats up in a natural convection method, the uploaded portion is small, and the download to the board accounts for most, and the detailed heat dissipation mode is not exhausted in a wire feet or a ball on the board. same.
Improvement method of packaging thermal resistance can mainly transmit three ways of structural design, material properties, and external heat-dissipating devices. The maximum installed radiator is affected, but this will increase manufacturing cost and complexity. .
Design Calculation / Exissue Power Editor
Bipolar Transistor
BJT total dissipation power is PC = IEVBE + ICVCB + ICRCS ≈icvcb), And the PC is related to the output maximum AC power PO: PO = (DC power PD of the supply transistor) - (the power of transistor dissipation PC) = [η / (1-η)] PCαPC, i.e., output AC power and transistor The dissipation power is proportional (η = PO / PD is conversion efficiency). The dissipation of the transistor power (consumption) is heating, if the heat cannot be distributed in time, the junction temperature Tj of the set-based electrolysis is increased, which limits the increase in output power; the highest junction temperature TJM (generally 175oc The corresponding dissipation power is the maximum dissipation power PCM. In order to increase the PO, it is required to increase the PC, but the increase of PC is limited by the increase in junction. In order to make the junction temperature exceed TJM, it is necessary to reduce the thermal resistance of the transistor to reduce the thermal resistance RT; maximum dissipation power PCMα1 / RT. The maximum power dissipation power corresponding to the highest junction temperature is (PCMS ≥ PCM): When steady state, PCM = (TJM-TA) / RT; transient, PCMS = (TJM-TA) / RTS.
Improve PCM measures, mainly reduce thermal resistance RT and reduce ambient temperature Ta; at the same time, transistors increase in pulse and high frequency, the PC increases, the safety work area is expanded, and the maximum dissipation power increases. Large, output power is also improved.
MOSFET
The maximum output power is also limited by the heat dissipation capacity of the device: PCM = (TJM-TA) / RT, MOSFET's highest junction TJM is still set to 175oC, fever The center is at the channel surface of the vicinity, and RT is mainly the thermal resistance of the chip (thermal resistance requires the method of calculating the transmission line characteristic impedance).
Diode dissipation power
Three-pole dissipation power is also known to the maximum allowable dissipation power PCM, which means that the triode parameter change does not exceed the maximum current collector consumption when the allowable value is specified. Dispersive power. Dissipation power is closely related to the highest allowance of the transistor to be a close relationship between the maximum current and collector. The tonis temperature of the silicon tube is approximately 150 ° C, and the junction temperature allowed value of the ruthenium tube is about 85 ° C.
To ensure that the tubular temperature does not exceed the allowable value, the generated heat must be distributed. When the transistor is used, its actual power consumption does not allow more than the PCM value, otherwise the transistor is damaged due to overload.
The transistor of the dissipation power PCM is less than 1 W is typically referred to as a small power transistor, a PCM equal to or greater than 1 W, less than 5 W, is referred to as a medium power transistor, and a transistor equal to or greater than 5w is called a transistor. High power transistor.
